Abstract
Background
Beyond its role in bone health, vitamin D is known to have immunomodulatory effects including cell proliferation, differentiation and apoptosis. Delays in immune reconstitution following HSCT increase transplant-related toxicity. Several studies have explored the role of vitamin D deficiency after HSCT with mixed results regarding its impact on survival outcomes. Our aim in this study was to examine the impact of vitamin D deficiency prior to HSCT on transplant outcomes in patients who received a haplo-HSCT.
Methods
This retrospective study included consecutive patients who underwent haplo-HSCT at our institution between 02/2009 and 01/2021. Primary objectives were to assess progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) by vitamin D status at the time of transplant. Vitamin D deficiency was defined as vitamin D levels < 20 nmol/L within 6 months prior to transplant. Survival estimates were calculated using Kaplan-Meier method. Proportional cox hazards analysis was used to adjust for multivariable analysis (MVA).
Results
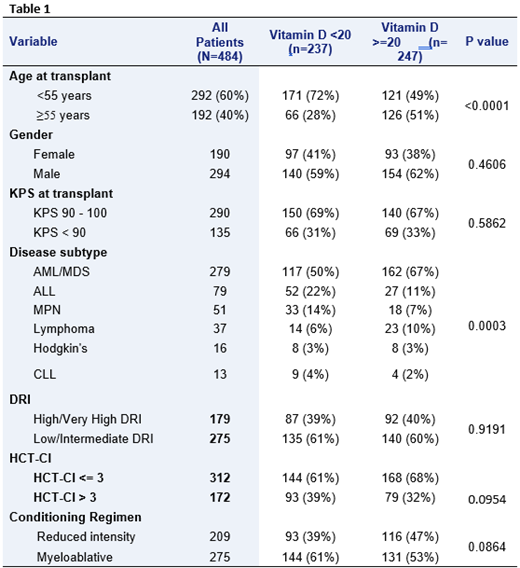
Four-hundred and eighty-four patients out of 508 patients had vitamin D checked at baseline and were included in the final analysis. Table 1 summarizes patient, disease, and transplant characteristics for all study patients, and by vitamin D status. Median age for all study patients was 48 (18-72) years, of which 237 (49%) had vitamin D deficiency and 247 (51%) had normal vitamin D level. Overall, the two groups were comparable, except that patients in the vitamin D deficiency group were younger in age. Furthermore, we adjusted for disease subtype heterogeneity by using the validated disease risk index (DRI). With a median follow-up of 35.4 (range, 1.4-132.8) months, the 3-year PFS and OS for all study patients were 44% and 48%, respectively. The respective 3-year PFS and OS for the vitamin D deficiency group were 42% and 47% compared to 46% and 50% for patients with adequate vitamin D (p=0.773 for PFS; p=0.704 for OS). Furthermore, we found no difference in non-relapse mortality at 3 years (each for 30%; p=0.6682). Univariate analysis (UVA) was performed for the following variables: vitamin D, age, gender, KPS, DRI, HCT-CI, and intensity of conditioning regimen. MVA included only the factors with p value<0.1 in in the UVA (plus vitamin D). In UVA for PFS, age ≥55, KPS <90, high/very-high DRI, HXT-CI >3 and reduced intensity conditioning were associated with inferior outcome. Same factors were significantly associated with inferior OS, but the reduced conditioning regimen. In MVA, age ≥55 (HR 1.627, 95% CI: 1.212-2.212; p=0.0013), high/very-high DRI (HR 1.865, 95% CI: 1.427-2.437; p=<0.0001), and HCT-CI >3 (HR 1.314, 95% CI: 1.001-1.726; p=0.0493) were associated with decreased PFS. Patients in the vitamin D deficiency group had a trend towards decreased PFS (HR 1.292, 95% CI: 0.975-1.712; p=0.0746), but this didn't reach statistical significance. In regard to OS, age ≥55 (HR 1.727, 95% CI: 1.278-2,334; p=0.0004), high/very-high DRI (HR 1.855, 95% CI: 1.396-2.467; p=<0.0001), and HCT-CI >3 (HR 1.411, 95% CI: 1.058-1.882; p=0.0191) were again associated with decreased OS, while vitamin D deficiency patients showed a trend for decreased OS (HR 1.312, 95% CI: 0.973-1.77; p=0.0753).
Conclusion
Our study demonstrates that serum vitamin D levels prior to haplo-HSCT have no significant impact on either progression-free or overall survival, albeit with a trend for worse outcomes in the vitamin D deficient group. Prospective controlled studies are needed to assess the impact of vitamin D deficiency on transplant outcomes, and on the role of vitamin D supplementation to improve the outcomes.
Qazilbash: Bristol-Myers Squibb: Other: Advisory Board; Oncopeptides: Other: Advisory Board; Angiocrine: Research Funding; Amgen: Research Funding; Biolline: Research Funding; NexImmune: Research Funding; Janssen: Research Funding. Shpall: Navan: Consultancy; Novartis: Honoraria; Axio: Consultancy; Magenta: Honoraria; Takeda: Patents & Royalties; Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals: Honoraria; Adaptimmune: Consultancy; Affimed: Patents & Royalties; Magenta: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal